The Transformative Impact of Nanotechnology on Lithium-Ion Batteries
Written on
Chapter 1: The Basics of Energy Storage
Nanotechnology is reshaping the landscape of lithium-ion batteries, leading to advancements that yield batteries which are not only more compact and lightweight but also possess greater energy density.
Graphic representation of a fully charged floating battery. Source: AlpakaVideo, via Storyblocks.
Many people are familiar with solar energy as a common source for powering homes. Some may even be aware of solar-powered vehicles. However, envisioning solar-powered aircraft might seem far-fetched. In reality, such technology is already in existence. The key to this innovation lies in the battery. Recent breakthroughs in nanotechnology have significantly enhanced the performance of our energy storage systems. Continue reading to learn more!
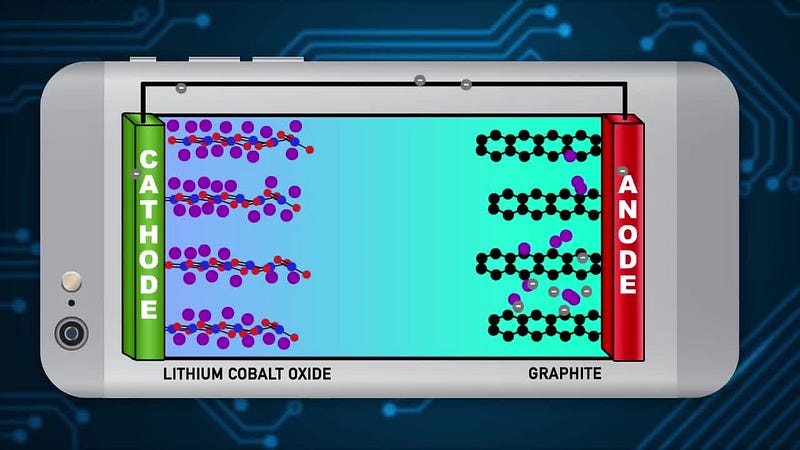
Illustration depicting the operational principles of batteries. Source: Reactions, via YouTube.
Section 1.1: Understanding Battery Functionality
To grasp how nanotechnology can enhance energy storage, it's essential to first understand the mechanics of batteries. A standard battery comprises multiple cells, each containing an electrolyte, an anode, and a cathode. When you connect the battery to an electrical device, activating the device generates a voltage between the anode and cathode. This voltage prompts electrons to flow through the connecting wires, providing power to the device. Simultaneously, positive ions travel through the electrolyte from the anode to the cathode.
The migration of positive ions and electrons to the cathode results in the formation of new molecules with other atoms present in the cathode. Once an excessive number of positive ions have migrated from the anode to the cathode, the battery is considered depleted and requires recharging to function again.
Subsection 1.1.1: Enhancing Battery Power Density
One crucial aspect of a high-performing battery is its power density, which refers to the amount of electrical power it can deliver relative to its weight.
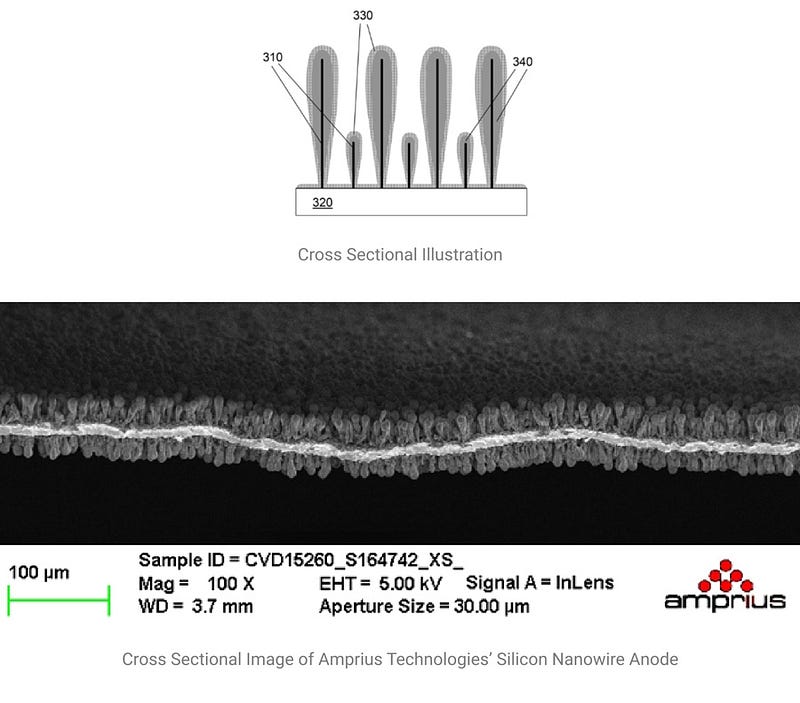
A cross-section and SEM image showcasing Amprius Technologies' silicon nanowire anode. The nanowire design accommodates safe swelling and contracting during charging cycles. Source: Amprius Technologies.
Currently, most batteries in use are lithium-ion types, which rely on lithium ions as the positive ions that move between the anode and cathode during operation. Nanotechnology presents an opportunity to boost the power density of traditional lithium-ion batteries. Amprius Technologies, for example, is pioneering lithium-ion batteries that utilize silicon nanowire electrodes.
Chapter 2: The Advantages of Silicon Nanowires
Defining the Role of Nanowires
In standard lithium-ion batteries, graphite serves as the anode material. In contrast, silicon can accommodate roughly ten times more lithium ions than graphite. Consequently, substituting graphite with silicon could potentially amplify the power density of conventional lithium-ion batteries by up to tenfold, resulting in significantly longer-lasting and lighter batteries.
Yet, if silicon is so advantageous, why has graphite been the prevalent choice for anode materials until now? The answer lies in the behavior of silicon during battery operation; when lithium ions are absorbed, the silicon anode expands, and it contracts when the lithium ions are released. This cyclical swelling and contraction can lead to cracking, causing the anode to fail.
Amprius Technologies has addressed this challenge by employing silicon nanowires rather than conventional silicon for the anode. The unique structure of silicon nanowires allows for safe volumetric changes during the charging and discharging processes. This innovation enables us to harness the superior power density of silicon while avoiding the risk of structural failure.
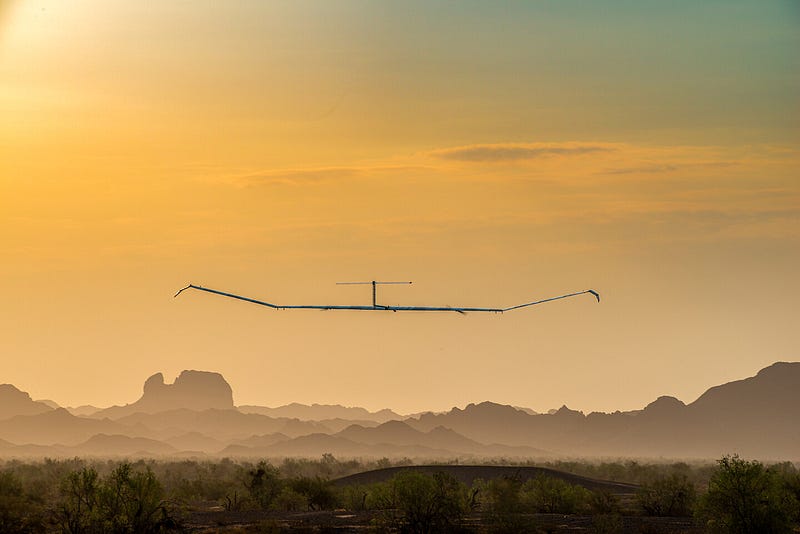

A photograph showcasing the Airbus Zephyr Solar High Altitude Platform System (S HAPS), utilizing Amprius' silicon nanowire batteries. Source: Airbus.
Amprius' silicon nanowire batteries are currently in use, with Airbus being a key customer. These batteries power the Zephyr S HAPS, a solar-powered aircraft capable of flying continuously for over 25 days at altitudes exceeding 70,000 feet. The advancements in energy storage technology have paved the way for the development of larger, more efficient, and powerful batteries. This is just the beginning—what further advancements can we anticipate in energy storage as nanotechnology evolves? Only time will reveal the answers.
The first video titled "This is Game Changing Tech for Batteries - Lithium Mining Explained" provides a comprehensive overview of how lithium mining is evolving with cutting-edge technology.
The second video titled "Using Nanotechnology to Improve the Performance of Batteries" delves into the latest advancements in nanotechnology and its implications for battery efficiency.
Enjoyed this article? Explore these related topics:
- What Is Nanotechnology and Where Is the Field Today? — A historical perspective on nanotechnology.
- 3 Ways Scientists Can Unlock New Technologies by Working at the Nanoscale — Understanding the significance of nanoscale research.
- Want to Make Contact with Aliens? Here’s How to Do It, According to Science — A discussion on scientific methods for potential alien communication.
Citations:
Boysen, Earl, and Nancy C. Muir. Nanotechnology for Dummies. Wiley & Sons, 2011.