Recent Discoveries of Planetary Anomalies in Our Solar System
Written on
Chapter 1: Unraveling Mars' Mysteries
Recent astronomical observations have unveiled peculiar phenomena on Mars, Jupiter, and Uranus. These findings, made possible by advanced instruments and observatories, enhance our understanding of the solar system's dynamics. This article delves into fascinating recent discoveries concerning our neighboring planet Mars and two distant gas giants, Jupiter and Uranus.
Let's begin with Mars. Planetary scientists have captured an extraordinary image of nearly perfect circular sand dunes on the Martian surface. While sand dunes on Mars typically display diverse shapes, these distinct circles stand out due to their unusual symmetry, with steep sides directed southward. According to the University of Arizona, which operates the High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRise) camera, this alignment suggests that Martian winds may be blowing the sand southward, although wind patterns on Mars can be quite variable. This image was taken on November 22, 2022, at coordinates 42.505 degrees latitude and 67.076 degrees longitude, as part of a series by the HiRise camera aboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).

In addition to the dunes, a set of images is being utilized to monitor the melting and retreat of frost on the Martian surface as winter comes to an end. While the featured image illustrates sand dunes devoid of frost, a previous image captures their frosty appearance.
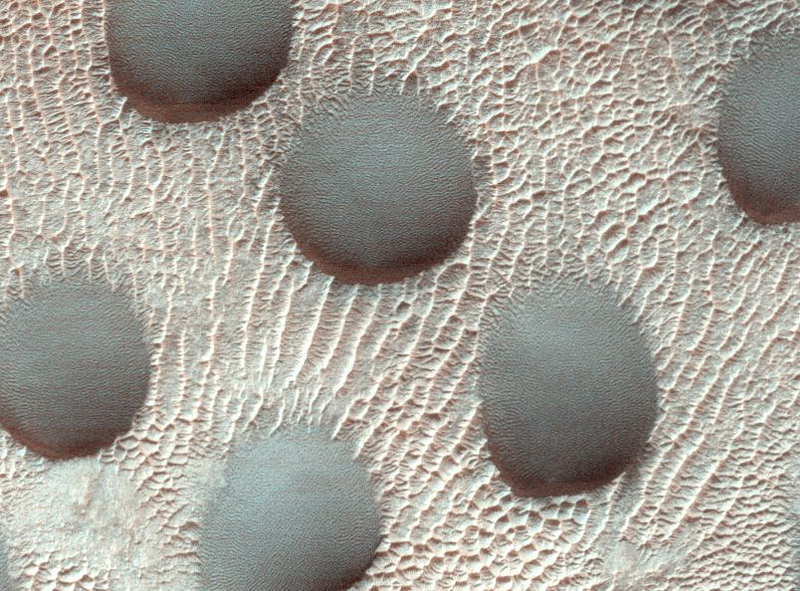
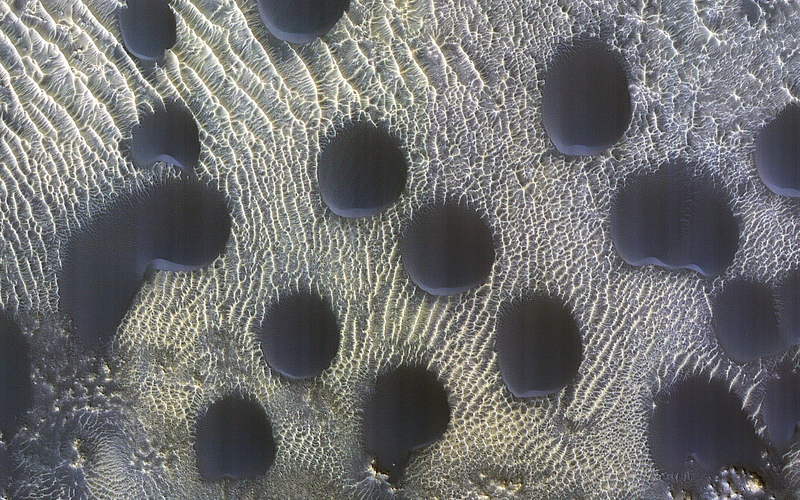
HiRise is monitoring 60 sites on Mars, having orbited the planet since the MRO's arrival in 2006. This camera is focused on the dedicated study of Martian sand dunes, collecting data throughout the Martian year (which spans 687 Earth days) to observe dune movement. Findings indicate that these dunes advance at rates of up to 3.3 feet (1 meter) each Martian year, from the equator toward the poles. Furthermore, HiRise is investigating glacier-like structures on Mars, examining crevasses that indicate their surface features.
By aggregating numerous observations over time, scientists are better understanding the mechanics of fractures found in "viscous flow features" at the bases of Martian slopes. These deposits are believed to have once contained significant ice, although its origin remains a mystery.
Chapter 2: Insights from Jupiter and Uranus
The Hubble Space Telescope has also delivered new insights into Uranus and Jupiter, showcasing atmospheric changes on these massive, distant planets. Unlike the dynamic weather patterns on Earth, the atmospheres of the outer solar system planets are relatively stable. However, examination of Hubble's images taken years apart reveals that these planets experience significant atmospheric transformations.
Recent images of Uranus taken between 2014 and 2022 have shown the development of a smoggy cap forming around its northern pole as it approaches its summer season. The 2022 image displays a white cap caused by a "photochemical haze," similar to the smog over urban areas on Earth, according to the Space Telescope Science Institute. While Hubble has been tracking this cap's growth for years, collecting data on Uranus remains challenging due to its extended seasons.

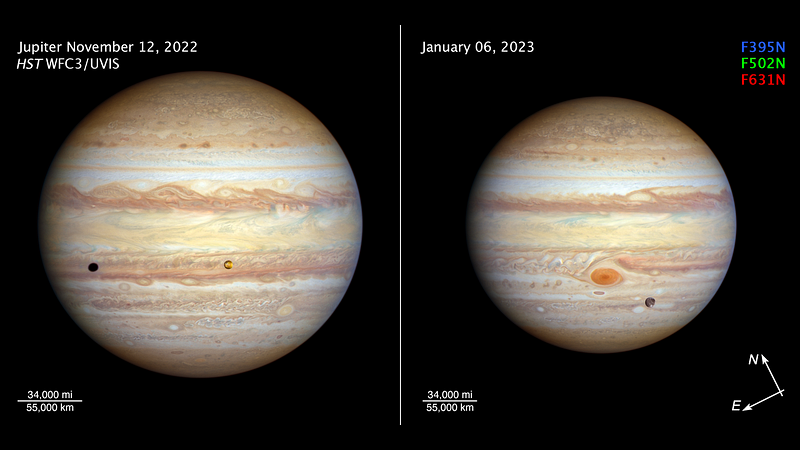
Turning our attention to Jupiter, the Hubble Space Telescope has captured intriguing images revealing notable weather patterns on the largest planet in our solar system. The Great Red Spot, a colossal storm observed for over 150 years, has reached its smallest recorded size. This storm, located in Jupiter’s southern hemisphere, boasts wind speeds of up to 270 to 425 mph (430 to 680 kph).
Hubble's recent images also depict a new stormy region forming north of the equator, featuring interlocking cyclones that spin in alternating directions—a phenomenon referred to as a "vortex street." Though there is speculation about this area potentially merging into a larger storm than the Great Red Spot, scientists believe this is unlikely. Hubble has been monitoring Jupiter since the 1990s, but the detection of these cyclones has only emerged in the past decade.
Stay informed with the latest astronomical discoveries. Join my mailing list for more insights and updates.