The Pursuit of Happiness: Insights from Ancient Wisdom
Written on
1. Happiness Formula
The formula for happiness can be expressed as:
- H = S + C + V
- H represents happiness
- S stands for biological set point
- C denotes life conditions (age, noise, commuting, relationships, control)
- V signifies voluntary activities
2. Is Happiness the Evolutionary Norm?
- No, as there are instances where individuals prioritize prestige over happiness, as discussed in the gene-centered view of evolution.
3. General Divisions in Happiness
The book outlines various divisions:
- Mind vs. Body
- Left vs. Right Cerebral Hemisphere
- Triune Brain
- Controlled (System 2) vs. Automatic (System 1)
- Consciousness versus Subconsciousness
- System 1 influences System 2
Self-Improvement
Understanding Happiness
1. What State Produces the Most Happiness?
- Flow is a key state of happiness.
- In this experience, the mind and body are in sync.
- Key components of flow include:
- Immediate feedback
- Perception of success potential
- Immersion in the experience that diminishes other needs
- Related concept: Self-determination theory (particularly aspect 2).
2. Conditions vs. Voluntary Activities
- Adaptation effects are crucial to understanding happiness.
- Individuals may or may not be sensitive to these effects, such as returning to baseline happiness.
- Conditions impacting happiness may include age, gender, and disabilities.
- A significant factor to avoid adaptation in happiness is variety.
3. The Impact of Commuting on Happiness
- People often adjust to larger living spaces but struggle with longer commutes.
- This short-lived increase in happiness is noteworthy.
- A longer commute does not always equate to reduced happiness, as ideal driving conditions can offer enjoyment.
Mindfulness and Meditation
1. Meditation as a Mental Health Pill
- Meditation (and likely mindfulness) can:
- Alleviate anxiety
- Boost contentment
- Enhance self-esteem and empathy
- Improve memory
2. Mindfulness vs. Gambling
- The more one engages in the pursuit of achievements, the more one risks losing (akin to gambling).
- Stepping away (mindfulness) is the key to winning.
Miscellaneous Insights
1. Pre-Goal and Post-Goal Attainment
- Positive affect before achieving a goal stems from the pleasure of progress.
- Post-goal attainment brings contentment, linked to activity in the left prefrontal cortex.
2. Affective Forecasting
- Humans are often inaccurate in predicting their future emotional states.
- There is a tendency to overestimate the intensity and duration of emotional reactions.
3. Apatheia
- This term denotes a calm state of mind, best translated as equanimity.
Neuroscience
1. Hemispheric Influence in Relationships
- The right hemisphere plays a primary role before the left in romantic interactions.
- The left hemisphere rationalizes actions initiated by the right.
2. Neocortex and Limbic System Interaction
- The neocortex enhances the limbic system's functioning.
Neuropsychology
1. Emotional Responses
- Anger and disgust are linked to the frontal insula.
2. Fairness Perception
- The perception of unfairness activates specific brain regions during reasoning.
3. Timing of Reinforcement
- Immediate reinforcement following behavior is most effective for learning.
Emotional Brain Dynamics
1. The "Elephant" Analogy
- The elephant represents the pessimistic aspect of our emotional brain, emphasizing the evolutionary advantage of being wary of threats.
Pharmacotherapy
1. Prozac and Neural Growth
- Prozac may enhance the level of a neural growth hormone in the hippocampus.
Neurophysiology
1. Threat Response
- The amygdala reacts more swiftly to negative stimuli compared to positive ones.
Frontal Lobe Activity
1. Asymmetry in Emotional States
- Activity levels in the left frontal cortex correlate with resilience to negative emotions.
Psychology
1. The Role of Hypocrisy
- Hypocrisy complicates reciprocal relationships.
2. The Interdependence of Happiness
- Happiness is influenced not just by oneself but also by social connections.
Psychotherapy
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
- This therapy interrupts negative thought cycles to foster positive feedback.
Self
1. Personality and Neural Competition
- The interaction between behavioral inhibition and activation systems leads to neural competition.
2. Causes of Violence
- Factors contributing to violence include moral idealism and high self-esteem.
Understanding Happiness
1. Heritability of Happiness Levels
- Happiness levels show high heritability, but progress is still possible through various means.
2. Age and Happiness Correlation
- Generally, older individuals report higher happiness levels.
Emotions
1. Pleasure vs. Gratification
- Pleasure involves immediate sensory enjoyment, while gratification arises from meaningful engagement.
Men and Women
1. Gender Happiness Discrepancies
- Despite experiencing higher depression rates, women also report deeper joy.
Developmental Psychology
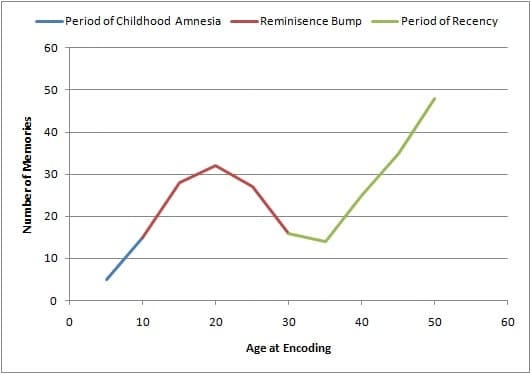
1. Adversity Hypothesis Timing
- This hypothesis is most effective during the reminiscence bump, a period marked by strong memory retention.
Research
1. Patience in Children
- Children exhibit patience by distracting themselves during tasks like the marshmallow test.
2. Chronic Noise Adaptation
- Individuals exposed to new, persistent noise rarely fully adapt.
Miscellaneous Insights
1. The Impact of Mints on Tips
- Offering mints can enhance tips through the principle of reciprocity.
Biopsychology
1. Heritability and Happiness Range
- Happiness operates within a potential range influenced by various factors.
Physiology
1. Gut-Brain Connection
- The enteric nervous system can trigger anxiety by signaling the central nervous system during gut infections.
Sociology
1. Character Evaluation Metrics
- It is estimated that 25 acts of heroism may balance out a single act of murder.
2. Theory Y and Worker Happiness
- A higher sense of control for workers can lead to increased happiness.
Happiness
1. Interpersonal Relationships
- These relationships typically have the most significant influence on happiness.
Microsociology
1. Moral Hypocrisy
- Individuals often prioritize the appearance of morality over actual moral behavior.
2. Conspicuous Consumption
- This refers to visible markers of success that individuals may display.
Macrosociology
1. Religion and Stability
- A lack of religious or cultural grounding can lead to feelings of instability and subsequent stress.
Ultrasociality
1. The Balance of Gratitude and Vengefulness
- Both traits are necessary to maintain social cooperation and avoid exploitation.
2. The Role of Gossip
- Gossip plays a crucial role in fostering cooperation within social groups.
3. Language as a Replacement for Grooming
- Language has evolved to replace physical grooming as a bonding mechanism in humans.
Dunbar’s Number
Culture
1. Humans as Cultural Beings
- Culture plays a significant role in human evolution, complementing genetic factors.
2. Self-Perception Across Cultures
- Cultures that emphasize collectivism may lead to more realistic self-assessments.
1. Social Group Size and Brain Size