Monitor Your System Efficiently with Btop: A Comprehensive Guide
Written on
Chapter 1 Understanding System Monitoring
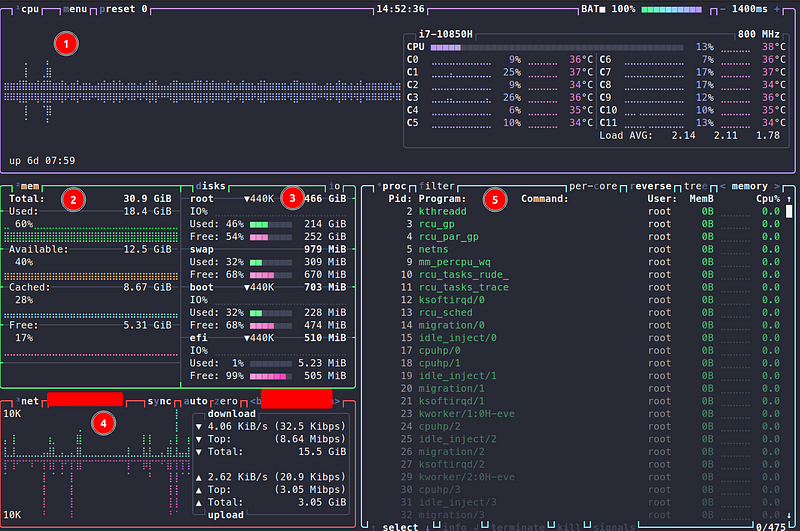
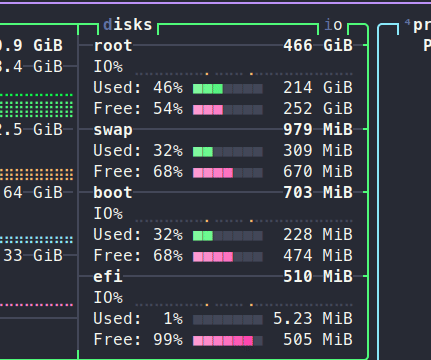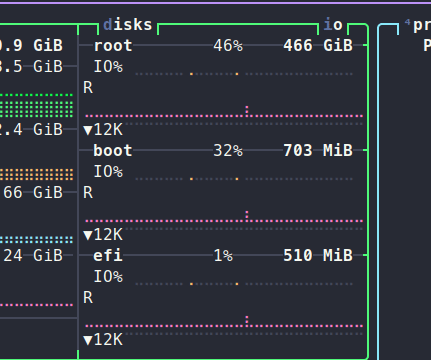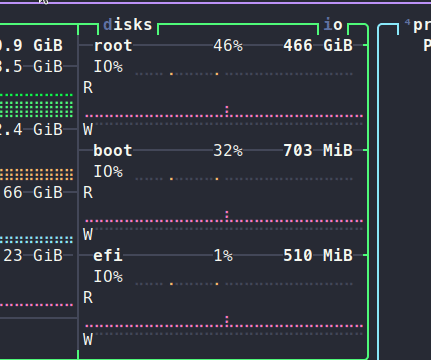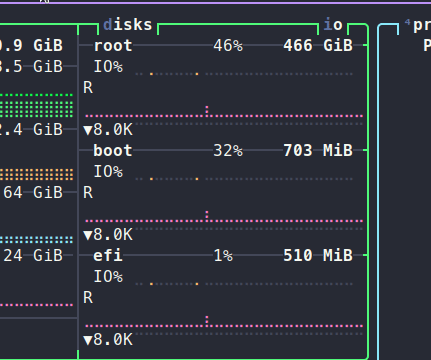
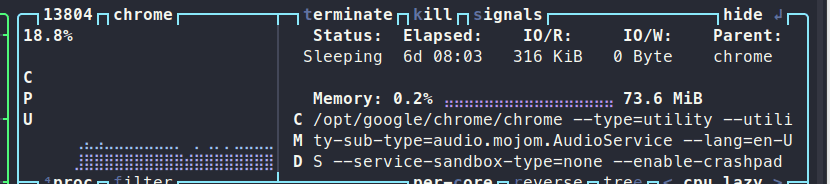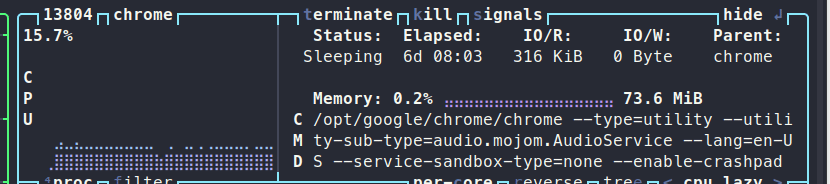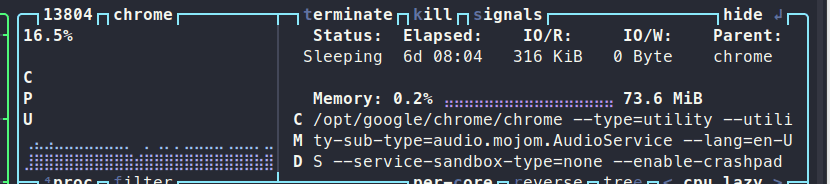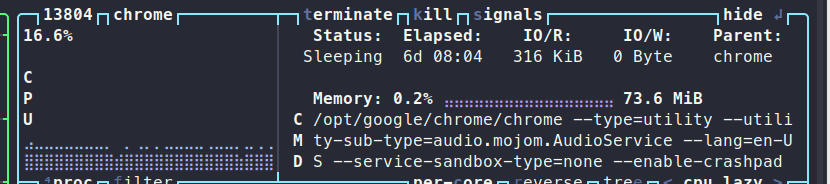
Monitoring your system's performance is crucial, especially if you’ve noticed your computer lagging. While Btop might not provide a complete diagnosis, it highlights potential issues, such as processes consuming excessive CPU resources or a full swap partition. Traditional commands like ps, df, or swapon can be helpful, but Btop consolidates everything you need into a single interface.
Installation Process
You can install Btop through various package managers. For instance, on the latest version of Ubuntu, you can use the following command:
sudo apt install btop
Additionally, a snap package is available for easy installation. Btop is open source and can be installed directly from binaries; detailed instructions can be found in the GitHub repository. If you’re a Mac user, you can easily install Btop via Homebrew:
brew install btop
Unfortunately, Windows users currently have no support for Btop.
Chapter 3 Customization and Features
Btop is not only functional but also customizable. It includes twenty different color themes; I personally prefer the Dracula theme. You can adjust the UI to fit your preferences, such as disabling rounded corners or modifying the graph symbols and clock formats.
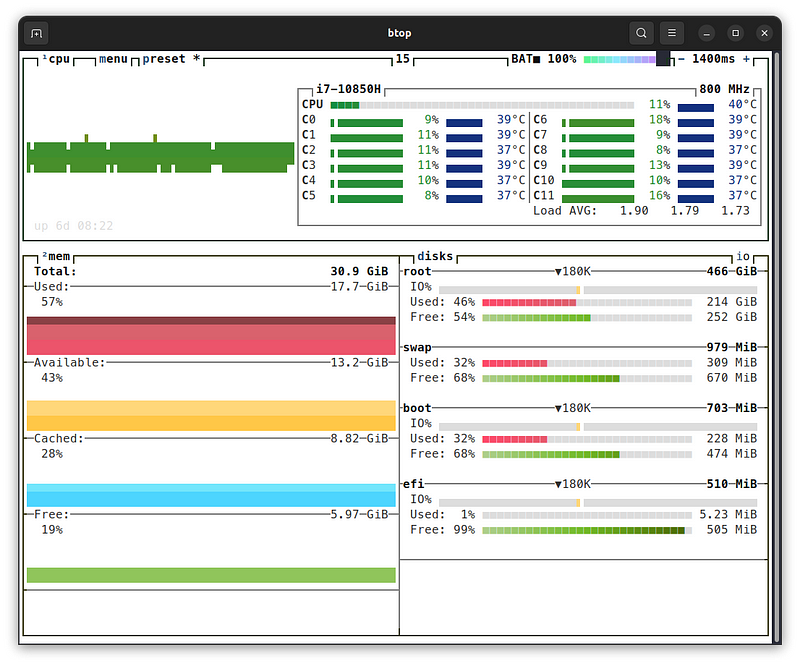
Moreover, you can alter the default settings of the panels, such as adding an extra graph to the CPU panel to display usage in alternative modes.
Btop also supports mouse interaction, allowing you to scroll through the process list using your mouse wheel. Configuration settings are saved in a file located at $HOME/.config/btop, making it easy to share your presets with colleagues. You can even create your own themes by following the format available on GitHub and placing them in $HOME/.config/btop/themes.
Recap and Resources
In summary, Btop serves as a versatile tool for monitoring your machine's resources. I hope you find it as beneficial as I do. For more information, here are some useful links:
- Btop’s GitHub repository
- Homebrew for Mac
- Information about Linux memory management
- Btop on SnapCraft
Thank you for reading!
Want to Connect? Subscribe to my newsletter to stay updated:
Explore amazing CLI dashboards like BTop++, Bottom, and Zenith for effective system monitoring.
Learn how to install BpyTop, the essential system monitoring command-line tool for Linux.