Exploring Abstract Explorer: AI-Powered Insights from PubMed
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Abstract Explorer
In the realm of scientific research, navigating through numerous abstracts can be daunting. To assist researchers, I previously introduced an application designed to analyze medical and scientific abstracts sourced from PubMed using artificial intelligence. This tool answers user inquiries by retrieving relevant abstracts. Today, I am thrilled to unveil a revamped version that employs one of OpenAI’s latest language models. This iteration provides enhanced prompt engineering to accurately interpret user questions within the context of the obtained abstracts, offering greater control over search parameters and improved response quality. If you're interested, you can obtain your API key from OpenAI and give it a try.
The initial application leveraged GPT-3 for generating responses but came with limitations. With the rapid advancement of natural language processing, particularly through models like GPT-3, these systems can produce highly persuasive and informative content. However, they can also generate misleading or incorrect information, emphasizing the need for verification. In response to user feedback, I completely redesigned the app, now named Abstract Explorer, to enhance its functionality and user experience.
Section 1.1: Key Features of Abstract Explorer
Abstract Explorer acts as a chatbot powered by GPT technology, exclusively using information extracted from PubMed abstracts to answer questions. This new version enables users to determine the number of abstracts to analyze, whether to narrow the search to review articles, and utilizes GPT-3.5-turbo—the actual model behind ChatGPT. While I did consider using GPT-4 for this application, I found that the answer quality was comparable, making it a less cost-effective option.
Subsection 1.1.1: Getting Started with Abstract Explorer
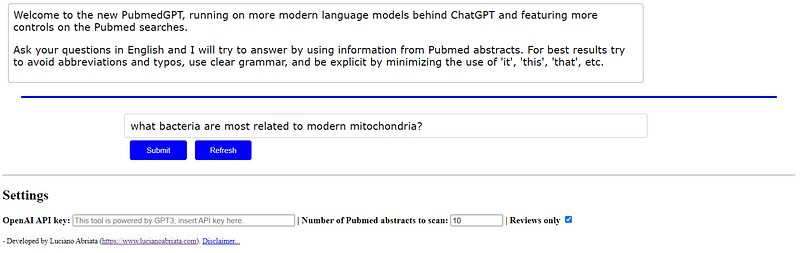
The Abstract Explorer web app is available at no cost, though it requires an API key from OpenAI, which may include some free credits. The interface is user-friendly, allowing seamless access to the tool.
Chapter 2: Understanding PubMed
PubMed serves as a vital online database of biomedical literature, managed by the National Institutes of Health in the United States. It encompasses a vast collection of peer-reviewed research across various domains, predominantly within the life sciences. By tapping into PubMed, Abstract Explorer can deliver more precise and in-depth scientific insights compared to standard GPT-3 capabilities. The database is equipped with APIs that facilitate programmatic searches for relevant articles and retrieval of their abstracts.
Here are some examples of the program's output based on user queries:
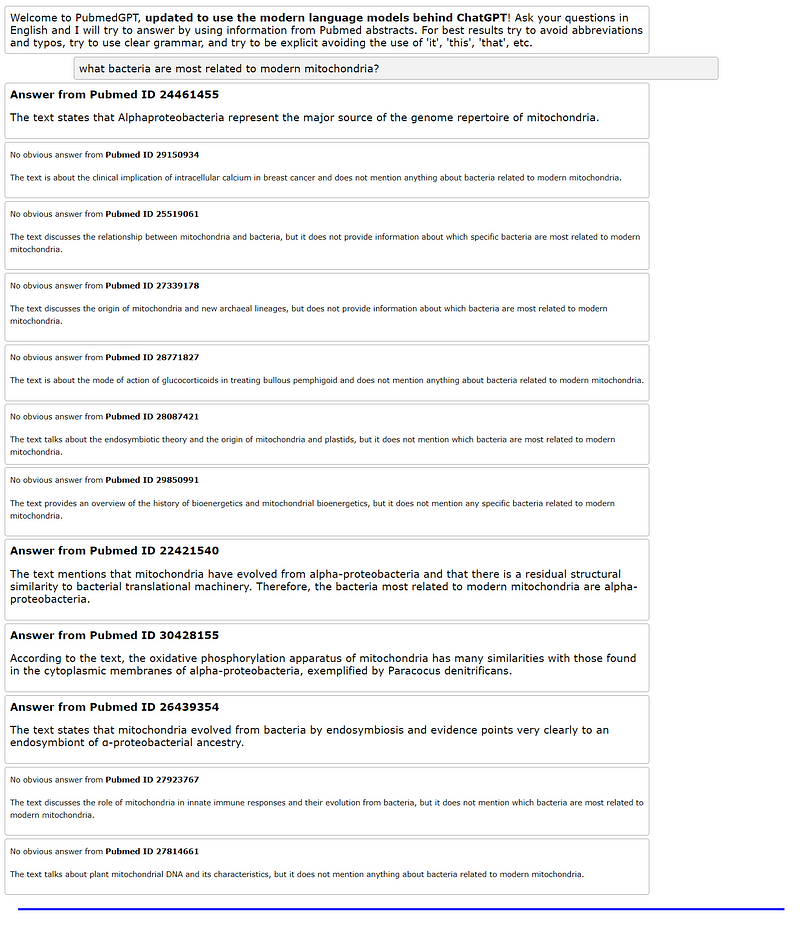
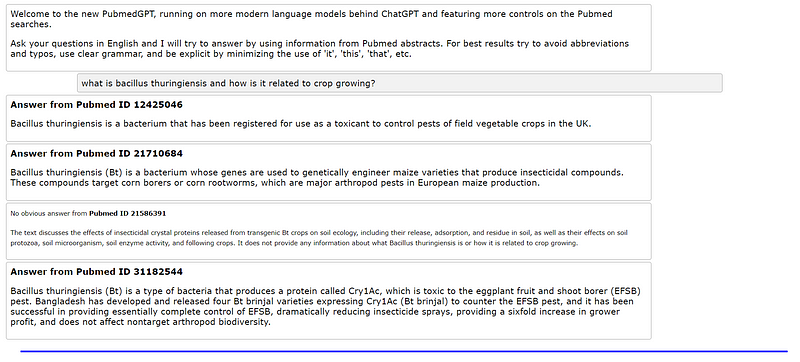
The tool is capable of gathering information even when user instructions are not highly specific:

I welcome your feedback on additional features you would like to see implemented. Perhaps you desire more control over PubMed searches or a final summarization of results from the retrieved abstracts? Any thoughts or ideas are greatly appreciated!